The automotive industry is embracing new technologies in its operations at a striking scale. In addition to technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and big data and analytics that have been around for a while, newer technologies such as Blockchain and the Internet of Things also find a multitude of applications in automotive. Here is a list of nine industry trends that are sure to blow your mind:
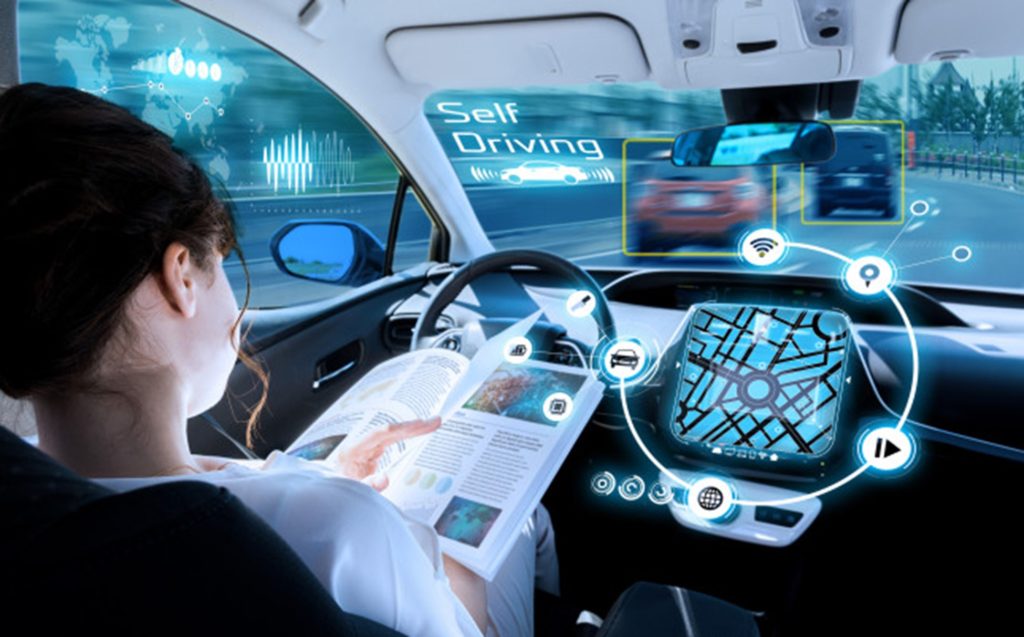
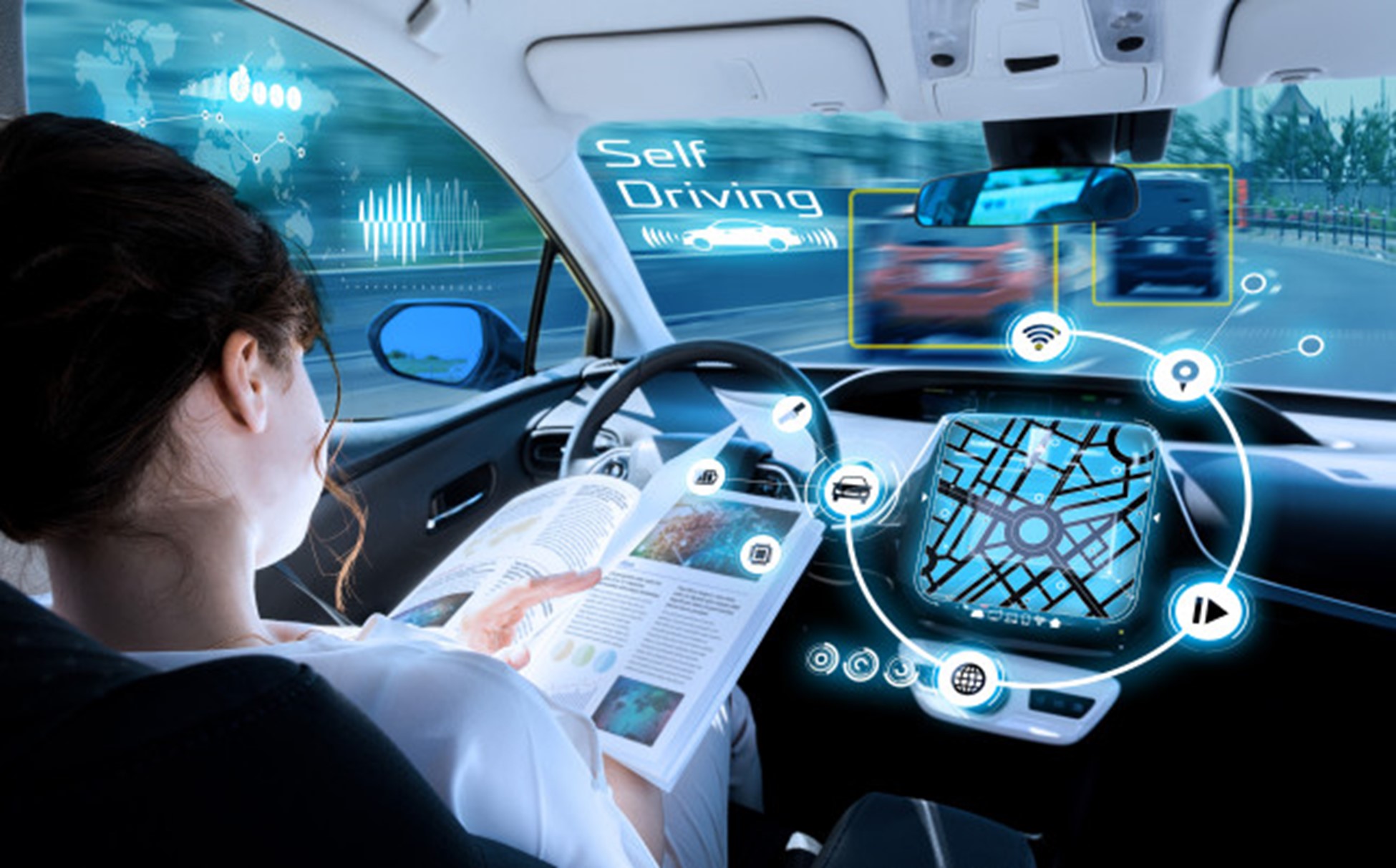
1. Autonomous Vehicles (AVs)
Self-driving or autonomous vehicles reduce the need for human drivers and have the potential to transform everyday transportation. Fleets of AVs expand the scope of last-mile deliveries, reduce downtime, and aim to make public transportation relatively safer. AVs are equipped with advanced recognition technologies, such as AI-enhanced computer vision to identify obstacles along the route.
If you think that seeing AVs in the streets is direct out of a sci-fi movie, think again! Companies like Waymo One from Google now offer a driverless taxi service which you can access through Google Maps in the Metro Phoenix area and San Francisco[1]. Other companies like GM aim to market personal autonomous vehicles directly to the public all the way to full level 4, level 5 autonomy by 2030[2].
2. Vehicle Connectivity
At present, vehicles come with a tamper-proof digital identity that is unique. This allows easy tracking of vehicular data for various purposes such as insurance, driver safety, predictive maintenance, and fleet management. Sharing vehicular data is not only beneficial to the individual customer, but also helps revamp the entire mobility ecosystem. Startups and scaleups develop vehicle connectivity solutions that enable them to connect and exchange data with other vehicles (V2V), an electric vehicle grid (V2G), public infrastructure (V2I), as well as with new and emerging ways to utilize vehicle data (V2X)[3]. Take the example of the Israeli startup NoTraffic which has developed a real time, plug-and-play autonomous traffic management platform that uses AI to reinvent how cities run their transport networks. The data of all road users is streamed and processed in real-time for smart mobility.
3. Electrification
Electric vehicles (EVs) are an excellent solution to the scarce fossil fuel reserves and the pollution caused by their use. However, there are still some issues that EVs need to address for greater adoption, such as high price, poor battery, inadequate charging infrastructure, fleet electrification, as well as powering renewable energy-based charging grids. Several startups in the industry are already tackling these challenges. For example, ChargeX offers a modular EV charging solution that converts parking spaces into charging parks for plug-in hybrids and electric cars.
4. Shared Mobility
With connected vehicles, new business models have come up that focus on shared mobility rather than on the traditional vehicle ownership model. This enables mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) and discourages unused vehicles. Did you know that in general cars are in use by their owners around 3% of the time, while the remaining 97% they’re parked in a garage or on the street?[4]
5. Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision find applications in robotic automation within the automotive industry. These guide self-driving cars, manage fleets, assist drivers to improve safety, and even help improve services such as vehicle inspections. AI is also key to automotive manufacturing, where its implementation results in faster production and a reduction of costs.
6. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI)
As self-driving cars and connected cars help evolve the automotive landscape, it will fundamentally transform how drivers interact with vehicles. Human-machine interfaces use voice-based or haptic feedback to operate vehicles. These expand the scope of how and what aspects of a car users control. Smart virtual assistants, another form of HMI, help drivers and riders interact with the vehicles and other service providers.
7. Blockchain
Blockchain facilitates multiple applications in the automotive industry. These include sharing vehicle data over a secure network for connectivity and shared mobility solutions such as ride-hailing, urban transportation, and deliveries. Moreover, blockchain technology helps verify the supply chain of spare parts or makes sure that raw materials and spare parts are from legal and trusted sources.
8. The Internet of Things
In the automotive industry, IoT enables secure communication between vehicles as well as vehicles and infrastructure components. The technology improves road safety, solves traffic congestion, and reduces pollution and energy expenditure with better fleet management[5]. Current emphasis is in developing advanced sensing technologies to gather more data about the vehicle as well as allow the vehicle to understand its surroundings- key for safety.
9. 3D printing
3D printing is gaining ground in different industries. Its key advantages are its flexibility, cost reduction, ease of customization and innovation potential. In the automotive industry 3D printing enables rapid prototyping with 3D printed models that accelerate the design and testing phases of production. It also allows manufacturers to print spare parts to match specific requirements. And last but not least, additive manufacturing of composite materials leads to automotive parts that are lighter and more durable.
In conclusion, technological innovations in the automobile industry are revolutionizing the driving experience day-by-day. It’s now becoming safer and more enjoyable to be on the road. However, should you need your windshield repaired, give us a call at 321.223.4106.
Useful terms:
Last-mile delivery: In a product’s journey from warehouse shelf, to the back of a truck, to a customer doorstep, the “last mile” of delivery is the final step of the process — the point at which the package finally arrives at the buyer’s door.
Blockchain: A distributed digital ledger that stores data of any kind. A blockchain can record information about cryptocurrency transactions, NFT ownership or DeFi smart contracts. While any conventional database can store this sort of information, blockchain is unique in that it’s totally decentralized.
The Internet of Things (IoT): Describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household objects to sophisticated industrial tools.
Scale-up: A company that has already validated its product within the marketplace and has proven that the unit economics are sustainable.
[1] https://techcrunch.com/2021/06/03/waymos-driverless-taxi-service-can-now-be-accessed-on-google-maps/
[2] https://techcrunch.com/2021/05/05/gm-ceo-mary-barra-wants-to-sell-personal-autonomous-vehicles-using-cruises-self-driving-tech-by-2030/
[3] https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/automotive-industry-trends-10-innovations-that-will-impact-automotive-companies-in-2020-beyond/
[4] https://www.forbes.com/sites/enriquedans/2021/06/11/the-future-of-autonomous-vehicles-product-orservice/
[5] https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/automotive-industry-trends-10-innovations-that-will-impact-automotive-companies-in-2020-beyond/